Criterion 6
GeoBoard belongs to the problem solving KITO From the curriculum documents I have choosen a level 2 and level 3 outcome, so as to cater for both grade 3 and grade 4 students in the classroom.
Relating student outcomes from the Technology Document are:
2.2 DESIGNING, MAKING AND APPRAISING: Devising - Generates designs that recognise some practical constraints using drawings, models and, where necessary, introducing some technical terms.
3.2 DESIGNING, MAKING AND APPRAISING: Devising - Generates designs that use a
range of graphical representations, models and technical terms.
Relating
student outcomes from the Mathematics Document are:
2.7b SPACE: Using spatial ideas, tools and techniques to interpret, draw and make - Pays attention to the shape and placement of component parts when interpreting and making drawings.
2.10 SPACE: Visualising, analysing and representing movements and transformations - Generates patterns and follows rules based on the simple repetition and movement of things.
3.10 SPACE: Visualising, analysing and representing movements and
transformations - Recognises and uses repetitions and movements of the same
shape embedded within arrangements and patterns.
* References
"Technology - a Curriculum Profile for Australian Schools ", produced by the Curriculum Corporation, 1994, Victoria, Australia.
"Mathematics - a Curriculum Profile for Australian Schools ", produced by the Curriculum Corporation, 1994, Victoria, Australia.
Criterion 7
PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
In relation to the criterion 7 and 8, the class at hand has completed a unit of work in the past on geometric shapes. They have a basic understanding of shapes such as squares, circles, triangles, prisms, cyclinder, hexagons, quadrilaterals, rectangles, parallelograms.
RESOURCES
For the following learning experiences on and off the computer the students will need the following tools: sheets of blank paper, sticky tape, scissors, pencils, rulers, erasers,
PREPARATION
Activity cards will need to be prepared and photocopied for each student, these include the snowman sheet, the shape sheet, the puzzle card, parallel pairs, comparing solids, and show my sides plus other shapes similar to these, GeoBoard patterns will need to be saved in the memory for children to use.
Learning Experience 1
Studens are asked to classify solids. They will be introduced to each type of solid as a whole class, solids such as prisms, cyclinders, cones, etc. This will be done by showing examples of solids and non solids. Discuss properties of type of solid and why it is or is not a solid of that type. Introduce them to the 'Comparing Solids' Activity Cards for completion. The following is an example of a cyclinder type activity card.
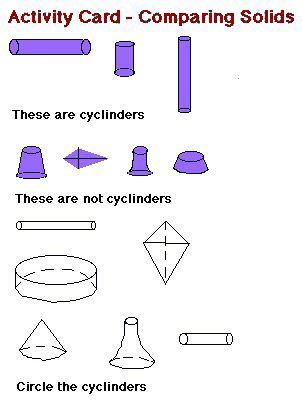
Learning
Experience 2
The difference between parallel and perpendicular sides is an important part of geometry. This would be taught in a whole class situation followed by another set of activity cards such as this:
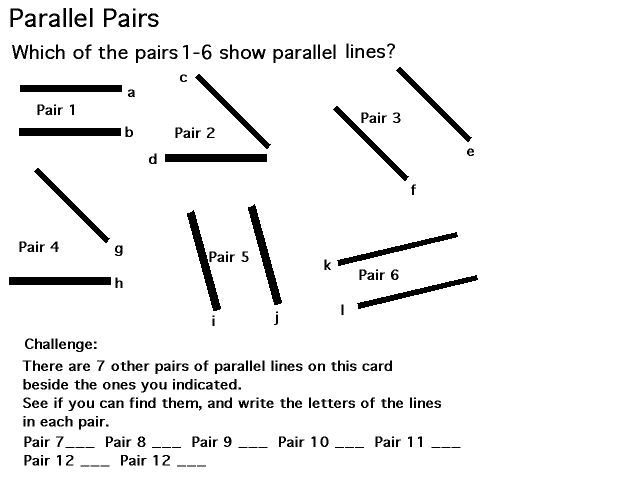
Learning
Experience 3
Students to construct from construction paper, a three dimensional shape, choosing from a list of shapes. The student will need to plan the design, cut it out correctly, and put together. Record steps of how they made their shape and share with the class. Note - students may need to spend research time in the library for construction instructions. Learning Experience 4 To introduce symmetry:
Ask the children to compare the following two snowmen: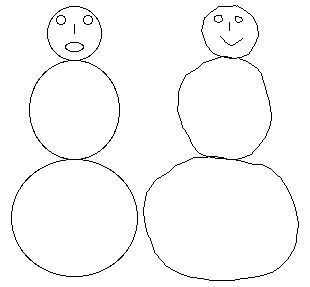
In order to check if they have choosen the right one, ask them to fold the drawing in the center to see if the sides match.
Learning Experience 5
The following activity card would then be presented to: Draw on the lines of symmetry on each shape; trace and fold the shapes to check your work; discuss with your partner why or why not each shape was symmetrical.
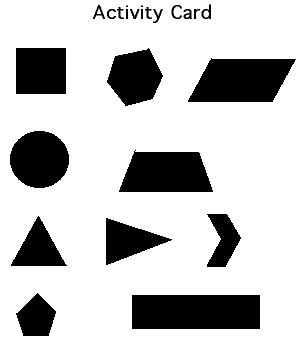
Learning Experience 6
Students to solve these puzzles using pattern blocks. Draw a sketch of the shape you make.
1 Use two different pieces; make a shape with:
Exactly 2 pairs of parallel sides. _____________________________
Exactly 1 pair of parallel sides. _____________________________
No parallel sides. ______________________________________
2 Use three different pieces; make a shape with:
Exactly
3 pairs of parallel sides. _____________________________
Exactly 2
pair of parallel sides. ______________________________
Exactly 1 pair
of parallel sides. ______________________________
No parallel sides.
_______________________________________
3 Using two of the same
piece, ________________________________
make a shape
4 What is the largest number of pair of parallel
sides of a shape you can make from:
2 pieces
?______________________________________________
3 pieces
?______________________________________________
4 pieces ?
______________________________________________
5 Can you put all
pieces together to make a shape with no parallel
sides?
______________________________________________________
There are many more learning experiences that could be done with this
unit of work, the above named were some of the planned learning
experiences.
Criterion 8
Learning Experience 1
After learning about the various shapes on the activity card, the following worksheet would be accomplished on the GeoBoard:
SHOW MY SIDES
Use a geoboard to show these figures:
1. Can you make a 4-sided figure with exactly two equal sides?
2. Can you make a 12 sided figure with all sides equal?
3. Can you make a 3-sided figure with three equal sides?
4. Can you make an 8-sided figure with four sides of one length and the other four of another length?
5. Can you make a 5-sided figure with exactly four equal sides?
6. Can you make a 4-sided figure with two pairs of equal sides that is not a parallelogram?
7. Can you make a 3-sided figure with two equal sides?
8. Can you make a 7-sided figure with no equal sides?
Learning
Experience 2
In order to practice symmetry work, the following activity would be saved in the GeoBoard memory. Students are asked to complete the pattern to make it a symmetrical design.
Learning Experience 3
Students to construct a symmetrical pattern, save the pattern, print it, explain how it was constructed. Before doing this, students will need to roughly plan their pattern before using the computer.
Learning Experience 4 Students to create a symmetrical pattern using a
single shape, save the pattern, print it, and explain how it was done. Students
will need to choose the shape and outline a pattern on paper, before using the
computer.
With the full version of GeoComputer, students can answer hundreds
of geometry problems and have fun doing it at the same time with the help of
GeoBot. This type of work can also lead on to using the Logo programme as an
extension to this unit.
Criterion 9
In our classroom there are four computers. They are grouped in pairs and are located in two learning centres, maths and reading. The maths reading centre is in front of the teachers desk, long a wall that has a door leading to the cloak room. The reading centre is located in a corner wall section along the front, across from the teacher's desk. There is a timetable for our computer use and it is as follows:
8:30am - 9:00 am: Children can play a range of educational games.
9:30am - 10:30am: This is spelling and maths time each day, children are rostered onto the computer during this time each day. However, every child must participate in the 5-10 minutes of basic maths fact sheet drills.
12:00pm - 12:30pm: Students are rostered over the week to communicate with their email pals.
1:30pm - 3:00pm: Groups are rostered on to do research or publishing for subject areas for projects in SOSE/health/science/language, etc.
3:00pm - 3:30pm: Children can play educational games.
Evaluations
As a teacher, I use spreadsheets to record evaluation marks and comments. I have created folders for each of the curriculum areas which contain spreadsheets for each unit of work. Each spreadsheet contains the names of all my students down the side and across the top are listed the outcomes that should be achieved by the end of the unit. After the outcomes, are listed the assignments/work that needed to be collected and assessed/projects/etc. For example with this current unit of work on Geometry, which would be contained in the maths folder, it would list all the outcomes (which are assessed for each student after all other work has been received), followed by headings such as these: Classification of solids; parallel lines activity sheet; constructed 3D shape; symmetry comparsion of snowman; shape symmetry; puzzle sheet; computer - show my sides; computer - complete symmetry; Computer - symmetry pattern; Computer - single shape symmetry.